Public health informatics is the systematic application of information and computer science and technology to public health practice, research, and learning. This course provides a broad overview of the field, taking account of classic public health information delivery, core principles of epidemiology, health inequalities and health behaviour change, as well as the implications of massive linked datasets for research and policy, and the value of emerging mobile and social technologies for healths surveillance.
Students will learn the application of informatics skills and knowledge to health related problems. Application activities will include simple data analysis and visualization of clinical data, answering clinical questions using information retrieval methods, and doing simple association analysis of gene variants and disease.
Objectives
The objectives of the course are to:
1. discuss problems and challenges that health informatics addresses;
2. describe the theoretical and practical foundations of health informatics;
3. provide basic skills and knowledge in health informatics in relation to future health-related careers;
4. discuss ethical and diversity issues in health informatics;
5. Explain how information and communication technologies are changing healthcare services and provision of health information;
6. discuss key issues related to the adoption of health information technology systems (digital divide, health literacy, policy issues, privacy and security); and
7. Explore emerging trends in health informatics.
Learning Outcomes
On completion of the course, students should be able to:
1. Explain any five (5) problems and challenges that health informatics addresses;
2. apply basic knowledge to the research and practice of health informatics;
3. demonstrate at least six (6) basic skills in health informatics;
4. demonstrate ability to identify four (4) genomic variants associated with a disease phenotype and communicate this association;
5. perform visualization and simple analysis of a data set to assess difficulty of predicting cardiovascular risk in a synthetic patient dataset; and
6. analyze ethical and diversity issues in health informatics.
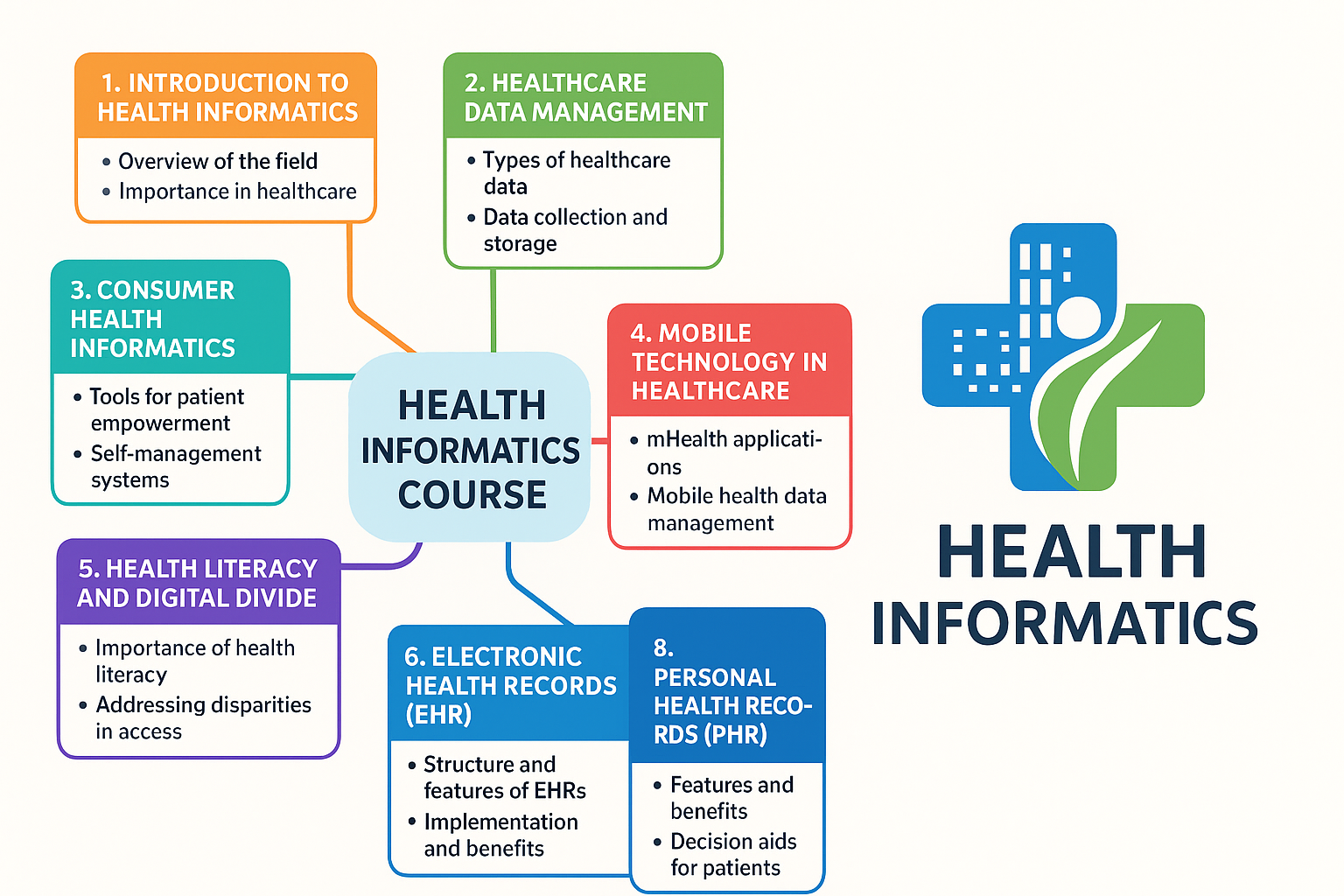
Course Contents
Overview of health informatics. Healthcare data, information and knowledge.
Consumer health informatics. Patient self-management and education systems.
Mobile technology and mhealth. Health literacy and digital divide issues.
Electronic health records. Health information exchange. Personal health records and decision aids.
Information retrieval (search) Evidence-based medicine and clinical practice guidelines. Clinical decision support systems and eprescribing. Clinical research informatics. Telemedicine.
Public health informatics disease management and disease registries. Patient safety and health information technology.
Bioinformatics (Demonstrate ability to identify genomic variants associated with a disease phenotype and communicate this association). Informatics Applications in Public Health.
Data Science, Analytics, and Visualization.
Ethical Issues in Health Informatics.
- Teacher: Aliyu Muhammad
